Are you struggling with thinning hair and wondering whether spironolactone vs finasteride for female hair loss is the right treatment for you? This article explains how each medication works, compares their effectiveness, and breaks down potential side effects and safety concerns.
You’ll learn what the latest clinical research says, how soon to expect results, and how to make an informed choice based on expert advice. This guide offers medically backed insights to help you regain confidence and make empowered decisions for your hair health.
Understanding Female Pattern Hair Loss
What Is Androgenetic Alopecia in Women?
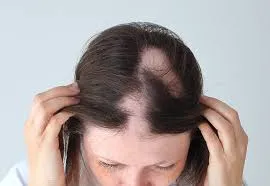
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL), or androgenetic alopecia, is a common condition marked by gradual thinning over the crown and widening part lines. Unlike male pattern baldness, women rarely go completely bald. FPHL typically begins in the 30s or 40s but can start earlier.
The Role of DHT and Hormones
At the core of FPHL is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that shrinks hair follicles and shortens the hair growth cycle. Women with hormonal imbalances (e.g., PCOS, menopause) are more susceptible. That’s why anti-androgen medications like spironolactone and finasteride are considered when over-the-counter treatments like minoxidil fall short.
Why Oral Pills May Be Needed
Topical treatments may not be effective for everyone, especially in moderate to severe cases. Oral medications offer a systemic approach, targeting the hormonal root cause of hair loss for better long-term control.
How Spironolactone and Finasteride Work
Spironolactone: Anti-Androgen Mechanism
Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic that also blocks androgen receptors and reduces testosterone levels. This dual action makes it especially effective in women with hormone-driven hair loss, including those with acne or hirsutism.
Finasteride: 5α-Reductase Inhibition
Finasteride works by inhibiting the enzyme 5α-reductase, which converts testosterone to DHT. By reducing DHT levels it prevents follicle miniaturization and helps maintain or regrow hair.
When Each Is Typically Prescribed
- Spironolactone is more commonly prescribed in premenopausal women, especially those with hormonal imbalances.
- Finasteride is typically prescribed off-label for postmenopausal women due to teratogenic risks in younger females.
Effectiveness & Clinical Evidence
Key Studies Comparing Spironolactone vs Finasteride
A 2023 randomized controlled trial found that both spironolactone and finasteride improved hair density in women with FPHL. However, spironolactone showed greater improvements in women under 45, while finasteride was more effective in postmenopausal women.
Data on Minoxidil Combination Benefits
Combining either medication with topical or oral minoxidil showed significantly better results in regrowth and reduced shedding, according to a 2022 systematic review. The combination approach tackles hair loss from multiple angles: hormonal and vascular.
Real-World Cases or Patient Stories
Many women report reduced shedding within 3–4 months of starting treatment, with visible regrowth around the 6–12 month mark. Patience and consistency are key.
Side Effects & Safety Profile
Spironolactone: Hyperkalemia, Menstrual Changes, Blood Pressure Effects
- Common side effects: Breast tenderness, dizziness, irregular periods
- Serious risk: Elevated potassium levels (hyperkalemia), especially in those with kidney issues
- Monitoring: Blood tests every 3–6 months for potassium and renal function
Finasteride: Sexual Side Effects, Teratogenic Risk
- Common side effects: Decreased libido, breast tenderness, mood changes
- Important caution: Teratogenic—must not be taken during pregnancy or by women planning pregnancy
- Monitoring: Pregnancy tests and patient counseling are required
Special Considerations: Pre-Menopause vs Post-Menopause
- Spironolactone is safer for younger women with menstrual cycles and hormonal acne.
- Finasteride is generally reserved for postmenopausal women to avoid pregnancy-related risks.
Dosage Guidelines & Treatment Charts
Spironolactone Dose Range: 50–200 mg/Day
- Start at 50 mg/day and increase gradually based on tolerance
- Optimal results are usually seen at 100–150 mg/day
- Take with food to reduce dizziness
Finasteride: 1 mg Daily (Off-Label in Women)
- Usually prescribed as 1 mg/day
- May be increased to 2.5–5 mg/day under supervision for postmenopausal women
- Consistency is key—don’t skip doses
Suggested Monitoring Schedule
| Month | Test Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Blood test, ECG | Baseline potassium, hormones |
| 3 | Repeat labs | Adjust dosage if needed |
| 6 | Clinical review | Evaluate regrowth progress |
Safe Contraception Protocols
Women of childbearing age must use effective contraception with finasteride. Spironolactone also requires caution due to hormonal interference.
Combination Approaches & Strategies
Adding Topical or Oral Minoxidil
Minoxidil boosts blood flow and extends the hair growth phase. Many dermatologists recommend using it in conjunction with oral medications to maximize outcomes.
Role of Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil (LDOM)
Recent studies support the safety and efficacy of low-dose oral minoxidil (LDOM) in women, especially those who find topicals irritating. It may be combined with spironolactone for synergistic effects.
Lifestyle, Nutrition, and PCOS Links
- Reduce stress and inflammation
- Ensure adequate iron, Vitamin D, and zinc levels
- Women with PCOS may benefit from spironolactone due to its anti-androgenic effects

FAQs
Can I switch from spironolactone to finasteride?
Yes, but consult your doctor. A washout period and hormone testing may be needed.
Does either medication affect fertility?
Spironolactone may affect ovulation. Finasteride is teratogenic. Use contraception as advised.
What if I experience excessive facial hair growth?
This is rare with spironolactone (usually reduces hair growth). Seek a dose adjustment if concerned.
How long do I need to stay on treatment?
Long-term use is usually necessary. Most women continue for 1–2 years minimum before tapering.
Is it covered by insurance?
Spironolactone is typically affordable. Finasteride for women may not be covered due to off-label use.
Are generic versions safe?
Yes, both medications are available in FDA-approved generic forms.
Take Your Next Step
If you’re unsure which treatment is right for your hair loss journey, book a personalized consultation with Dr. Rana Irfan in Islamabad today. Our team specializes in female hair restoration and hormonal management. Get expert guidance, tailored prescriptions, and ongoing support for visible results.
