Ever wondered is male and female hair different? You’re not alone. Though all human hair shares the same basic structure, there are notable gender-based differences in hair texture, growth patterns, and even hair loss susceptibility.
Understanding these distinctions can help you make smarter decisions about hair care, treatment, and products. In this guide, we’ll explore how male and female hair differs biologically and cosmetically, and why that matters for your scalp health, styling choices, and treatment outcomes.
Understanding the Basics of Hair Anatomy
Structure of Human Hair
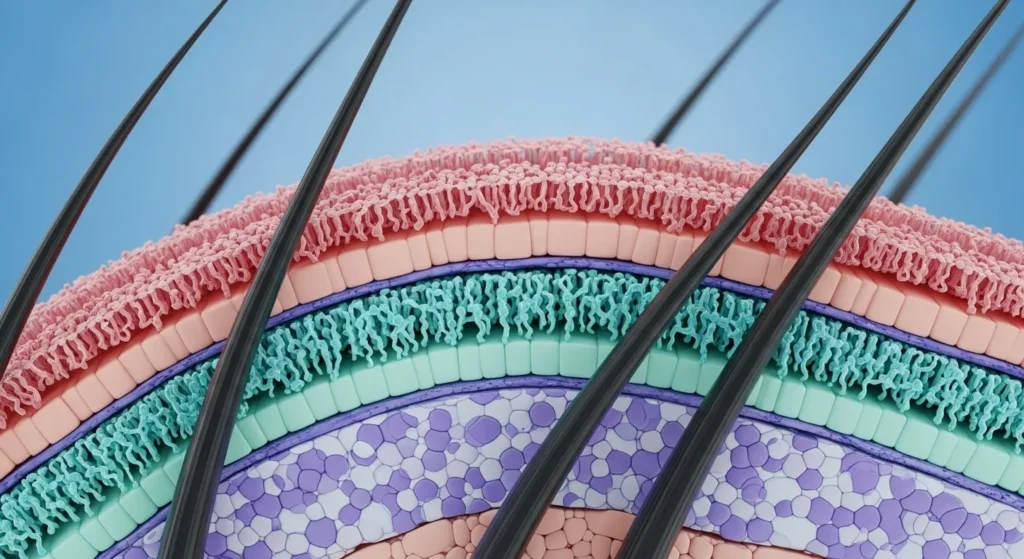
Hair in both men and women is made up of three layers: the cuticle (outer layer), cortex (middle), and medulla (innermost layer). It grows from follicles located in the dermis of the scalp and is primarily composed of keratin.
Hair Growth Cycle in Males vs Females
Both genders follow the same hair growth cycle—anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (rest)—but the duration of these phases can differ slightly.
- Women typically have a longer anagen phase, resulting in longer hair.
- Men may experience a shorter growth phase due to hormonal influences like DHT.
Hormonal Influence on Hair Development
Androgens, particularly testosterone and its derivative DHT (dihydrotestosterone), heavily influence male hair growth patterns. In contrast, estrogen helps stabilize hair growth in women, delaying thinning.
Key Differences Between Male and Female Hair
Hair Texture and Thickness
- Male hair is generally thicker and coarser, especially in areas like the beard or chest.
- Female hair tends to be finer and softer, particularly on the scalp.
Scalp Oil Production and Hair Type
Men usually produce more sebum (natural oil), which can make their hair appear greasier faster. This influences the type and frequency of shampooing needed.
Growth Patterns and Hairline Shape
- Men often develop a receding hairline or M-shaped pattern due to androgen sensitivity.
- Women retain a rounded frontal hairline but may notice thinning across the crown.
Hormonal Differences (Testosterone, Estrogen, DHT)
- DHT causes miniaturization of hair follicles in men.
- Estrogen has a protective effect on hair, especially during pregnancy, but hair shedding may increase after childbirth or menopause.
Hair Shedding and Growth Rate by Gender
Women may experience seasonal shedding and changes due to hormonal fluctuations, whereas men typically undergo more consistent patterns of hair thinning.
How Hair Loss Differs in Men and Women
Male Pattern Baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia)
Characterized by a receding hairline and thinning crown, male pattern baldness is primarily linked to DHT sensitivity. It affects over 50% of men by age 50.
Female Pattern Hair Loss
Often starts with diffuse thinning across the top of the scalp without complete baldness. Unlike men, women rarely lose all their hair due to hormonal balancing effects.
Differences in Diagnosis and Progression
- Men: Diagnosed through the Norwood scale.
- Women: Evaluated via the Ludwig scale or Savin scale.
Female hair loss is often multifactorial, involving stress, thyroid issues, and iron deficiency.
Common Misconceptions
- “Only men go bald.” (False)
- “Hair loss in women is always hormonal.” (Also false—can be due to nutrition, stress, or underlying medical conditions.)
Styling, Maintenance & Cultural Expectations
Hair Care Habits and Product Use
Women generally use more hair care and styling products, while men may prefer 2-in-1 shampoos or minimal routines. These behaviors can affect scalp health and hair quality.
Heat Styling, Coloring, and Grooming Differences
- Women: More frequent use of blow dryers, flat irons, and color treatments.
- Men: Greater likelihood of using clippers, gels, or wax-based products.
Hair as a Cultural or Social Identifier
Hair often holds cultural and personal significance, with different grooming standards for men and women across societies. This impacts how hair is styled, valued, and cared for.
Expert Insights on Gender-Based Hair Differences
Trichologist’s Explanation on Scalp Conditions by Gender
Men are more prone to seborrheic dermatitis due to higher sebum levels, while women may experience telogen effluvium more frequently due to stress or hormonal changes.
Clinical Data on Hair Growth and Thickness
Studies have shown that male terminal hair has a greater diameter, especially in androgen-sensitive areas like the beard or chest, while female scalp hair grows more uniformly but is finer.
Can Male and Female Hair Products Be Used Interchangeably?
Ingredient Formulation and Purpose
Gendered products often differ in fragrance and marketing, but active ingredients like biotin, caffeine, or ketoconazole work across genders. However, formulas may vary in pH and oil balance.
When Gendered Products Matter — and When They Don’t
If you have specific scalp issues (e.g., oily scalp in men, dry scalp in women), gendered products might help. Otherwise, many unisex formulations offer equal benefits.
Common Myths About Gender and Hair
“Women Don’t Go Bald”
Women do experience pattern hair loss, just in a diffuse form. It’s often underdiagnosed due to social stigma.
“Men’s Hair Grows Faster”
Hair growth rates are almost identical between genders (about 1.25 cm per month), though environmental and hormonal factors may cause variation.
“Gender Determines Hair Texture”
Hair texture is primarily determined by genetics and ethnicity, not gender.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is there a genetic difference in male and female hair?
Yes. While the basic hair structure is the same, gene expression influenced by sex hormones affects thickness, pattern, and hair loss.
Can women use men’s shampoo and vice versa?
Generally, yes. However, product choice should depend more on scalp type and condition than gender.
Do hormones really cause different hair behaviors?
Absolutely. Testosterone, DHT, and estrogen all have significant impacts on hair growth, shedding, and follicle sensitivity.
Is female hair stronger than male hair?
Not necessarily. Male hair is often coarser and thicker, but female hair may be more resilient to some types of breakage due to care routines.
Final Thoughts: Why These Differences Matter
Understanding how male and female hair differs helps you:
- Choose the right products for your hair type
- Address hair loss more effectively
- Avoid falling for myths or stereotypes
Whether you’re dealing with hair thinning or simply curious about your hair’s behavior, this knowledge empowers you to make informed, personalized decisions.
Want expert advice tailored to your unique hair type and gender-specific needs?
Book a consultation with Dr. Rana Irfan in Islamabad — Pakistan’s leading ABHRS-certified hair restoration specialist. Get a complete scalp analysis and discover treatment options designed just for you.
