Summary
How to Stop Hair Loss from Ulcerative Colitis? Hair loss from ulcerative colitis is a common issue caused by nutrient deficiencies, stress, and medications.
To stop hair loss from ulcerative colitis, focus on improving nutrition, managing stress, and adjusting medications. Incorporating treatments like minoxidil and exploring professional interventions can also support hair regrowth. Consult a specialist for personalised solutions and a tailored recovery plan.
Introduction
Experiencing hair loss while managing ulcerative colitis (UC) can be distressing. If you’re struggling with hair thinning or shedding, you’re not alone. Ulcerative colitis, a chronic inflammatory bowel disease, can trigger hair loss due to nutrient deficiencies, medications, and stress.
This article will guide you through why UC causes hair loss and how to stop it, offering actionable solutions to help restore your hair health. Learn how to manage UC-induced hair loss effectively and prevent further damage.
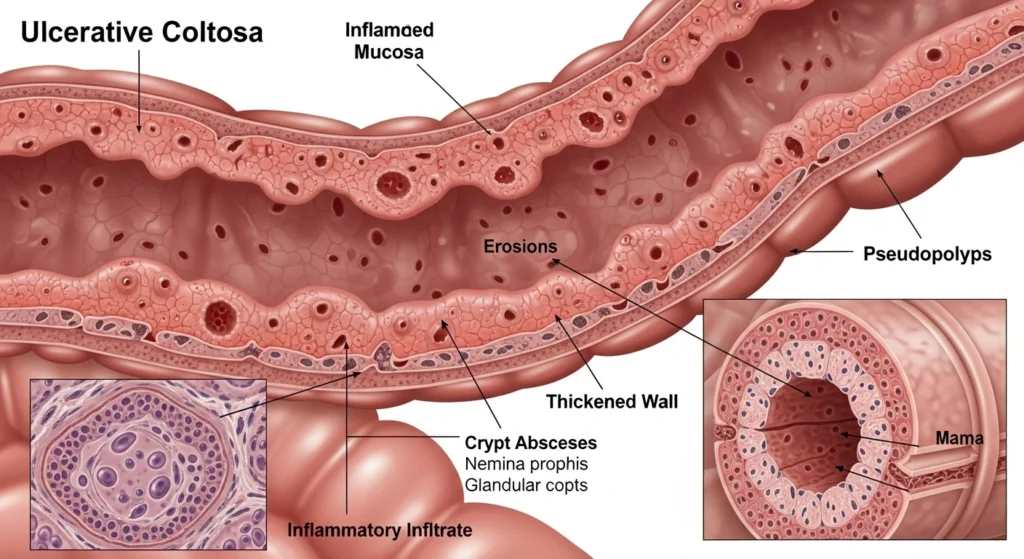
Understanding Hair Loss from Ulcerative Colitis
The Connection Between UC and Hair Loss
Ulcerative colitis affects the digestive system, leading to inflammation in the colon. This inflammation can cause malabsorption of essential nutrients like iron, protein, and vitamins, which are crucial for healthy hair. Without these nutrients, hair can become brittle, thin, and fall out. The body’s inability to absorb enough nutrients often leads to hair loss in UC patients.
Moreover, UC flare-ups can cause additional stress on your body. Stress has been proven to be a major factor in hair loss, particularly through conditions like telogen effluvium, where hair prematurely enters the shedding phase.
How UC Medications Can Contribute to Hair Loss
Many medications used to treat UC, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, are known to cause side effects, including hair thinning. These medications suppress the immune system to control inflammation, but can also interfere with the hair growth cycle. Hair loss may be temporary or persistent, depending on the type of medication used.
For example, corticosteroids, commonly prescribed during UC flare-ups, can cause telogen effluvium, a condition where hair prematurely sheds after being in the growing phase for too long.
The Role of Stress in UC-Related Hair Loss
Stress from UC flare-ups, frequent hospital visits, and the overall strain of living with a chronic illness can trigger hair loss. Stress causes an increase in cortisol, a hormone that can disrupt the hair growth cycle. It also contributes to other symptoms like fatigue, which can exacerbate the hair loss problem.
How to Prevent and Manage Hair Loss from Ulcerative Colitis
Focus on Nutrition: The Best Diet for Hair Health
Proper nutrition is crucial for combating hair loss. People with UC often struggle to absorb key nutrients, which can negatively affect hair health. To prevent or stop hair loss, it’s essential to focus on a nutrient-rich diet. Here are a few nutrients that are particularly important for hair growth:
- Iron: Low iron levels can lead to anaemia, which contributes to hair thinning. Include iron-rich foods like spinach, beans, and lean meats in your diet.
- Protein: Hair is made of protein, so getting enough is critical. Incorporate protein-rich foods like eggs, fish, and legumes.
- Biotin and Zinc: Biotin and zinc play a role in the hair growth cycle. Consider adding biotin-rich foods like nuts and seeds, as well as zinc-rich foods like oysters and pumpkin seeds.
If your UC makes it difficult to absorb these nutrients, a doctor might recommend supplements.
Managing Your Medications and Treatments
While medications are necessary to manage UC, certain drugs can contribute to hair loss. If you’re experiencing hair thinning due to your medication, consult your healthcare provider. There may be alternatives or adjustments to your treatment plan that can help minimise hair loss.
For example, switching to a different immunosuppressant or using corticosteroids for a shorter duration may help reduce hair loss. Discuss with your doctor about non-hair-thinning medication options.
Reducing Stress and Improving Mental Health
Chronic stress from UC can directly impact hair growth. Implementing stress management strategies is essential for overall well-being, including your hair health. Here are some ways to manage stress:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Regular mindfulness practices can help reduce the body’s stress response and lower cortisol levels.
- Exercise: Physical activity can improve circulation and reduce stress. Activities like yoga or walking are especially helpful.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who understand the struggles of living with UC can provide emotional relief and reduce stress.
By incorporating stress management techniques into your routine, you can help mitigate the effects of UC-related hair loss.
Expert Tips for Recovering from UC-Induced Hair Loss
Topical Treatments and Natural Remedies for Hair Growth
When dietary changes and stress management are not enough, topical treatments can provide support. Here are some options:
- Minoxidil: This over-the-counter medication has been proven to help stimulate hair growth in some people with hair thinning. It can be a helpful addition to your hair care routine.
- Essential Oils: Oils like rosemary, peppermint, and lavender are believed to support hair growth by improving scalp circulation. Consider massaging these oils into your scalp to promote hair health.
Always consult a dermatologist before using any new treatment.
Medical Interventions and When to Seek Help
If your hair loss continues despite managing UC and implementing lifestyle changes, medical intervention might be necessary. For severe hair loss, treatments like hair transplants or PRP (platelet-rich plasma) therapy might be options. These treatments work by stimulating hair follicles to promote regrowth.
Consult with a dermatologist or a hair restoration specialist to explore these options if your hair loss becomes significant.
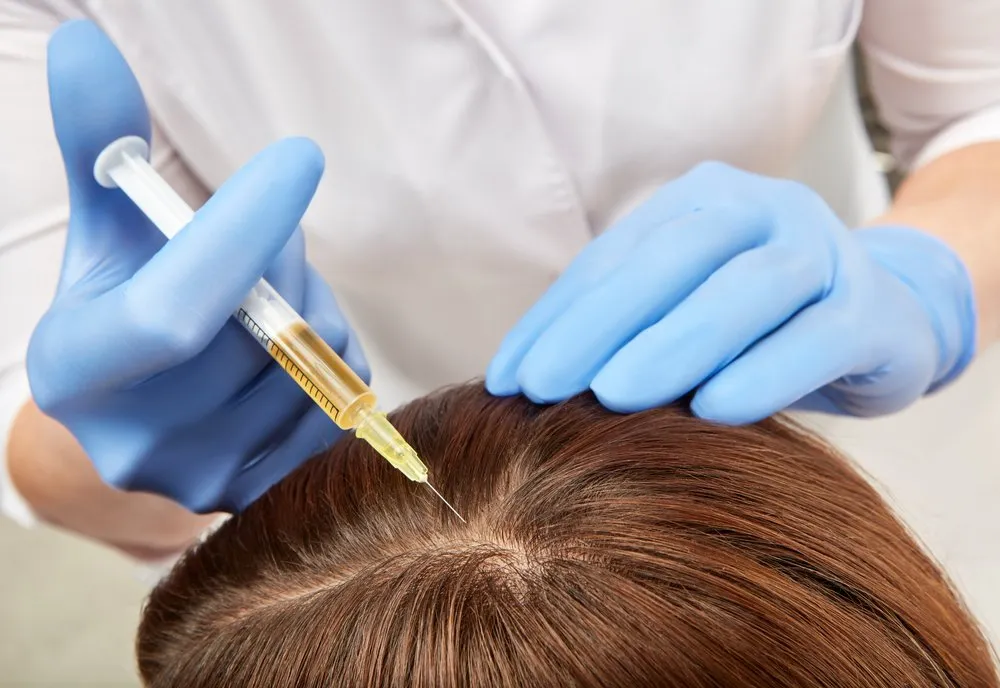
Lifestyle Adjustments for Healthier Hair
In addition to medication and nutrition, taking care of your hair with a gentle routine can reduce further damage:
- Avoid using harsh chemical treatments or excessive heat.
- Use a gentle shampoo and conditioner designed for sensitive scalps.
- Avoid tight hairstyles that can put stress on the hair follicles.
These small adjustments can help protect your hair and improve its overall health.
Recovery Timeline and Precautions
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
Hair regrowth after UC-related hair loss varies depending on the severity of the condition and how well you manage your UC. In general, if nutrient deficiencies are corrected and stress is minimised, you may begin to notice hair regrowth within 3–6 months. However, medications that cause hair loss may take longer to recover from.
When Can You Resume Normal Hair Care Routines?
Once hair regrowth begins, you can slowly reintroduce regular hair care routines. Avoid heavy styling products and heat for at least six months after hair loss recovery.
Long-Term Hair Care: Sustaining Results
Maintaining your hair’s health long-term requires ongoing care. Regularly monitor your nutrient intake, manage your stress levels, and stick to a gentle hair care routine. Periodically check in with your doctor to ensure that your UC treatment is not contributing to hair loss.
FAQs on Hair Loss from Ulcerative Colitis
Why Does Ulcerative Colitis Cause Hair Loss?
Ulcerative colitis causes inflammation and malabsorption of key nutrients like iron and protein, leading to hair thinning or shedding. Stress and medication side effects also contribute to hair loss in UC patients.
Can Stress Alone Cause Hair Loss in UC Patients?
Yes, stress from UC flare-ups can lead to hair shedding due to its impact on hormone levels, particularly cortisol.
What Nutrients Should I Focus on to Prevent Hair Loss?
Key nutrients for hair health include iron, protein, biotin, and zinc. UC patients should focus on a diet rich in these nutrients or consider supplements if malabsorption is an issue.
Should I Change My Medications to Stop Hair Loss?
If you’re experiencing significant hair loss due to medication, consult your healthcare provider. There may be alternative treatments or adjustments that can help reduce hair thinning.
How Can I Tell If My Hair Loss Is Due to UC or Another Condition?
If your hair loss persists despite managing UC symptoms, consider consulting a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis to rule out other causes of hair loss, such as alopecia or thyroid issues.
Next Steps
If you’re struggling with UC-induced hair loss, it’s important to take action sooner rather than later. Start by optimising your nutrition, managing your stress, and consulting your doctor about medication adjustments. If necessary, explore topical treatments or hair restoration options for more significant results.
To ensure a smooth and successful recovery from hair loss related to UC, book a consultation with our hair restoration specialist today. We’ll help you find the best approach to restore your hair health.
