Struggling with unexplained hair shedding? Gluten and hair loss may be linked—especially if you have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
In this guide, you’ll learn how gluten-triggered inflammation and nutrient deficiencies can impact hair growth, what recovery timelines look like, and expert-backed steps to restore healthy hair.
With real cases, clinical insights, and nutritional strategies, you’ll have the tools to take control of your hair health and work confidently with medical professionals.
Understanding Hair Loss & Gluten
What Is Gluten & How Is It Related to Gut Health?
Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. For most people, it’s harmless. However, in individuals with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, gluten can trigger inflammation in the small intestine, impairing nutrient absorption.
Since hair follicles rely on a steady supply of vitamins, minerals, and proteins, gut damage from gluten can indirectly lead to diffuse hair thinning, brittle hair, or even autoimmune-related hair loss.
Overview of Hair Loss Types Linked to Gluten
- Telogen Effluvium – Temporary shedding triggered by stress or nutrient deficiency.
- Alopecia Areata – Autoimmune hair loss, sometimes linked with celiac disease.
- Diffuse Thinning – Widespread hair loss due to chronic malabsorption.
How Celiac Disease Can Lead to Hair Loss
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition where gluten ingestion damages the small intestine’s lining. This leads to malabsorption of critical nutrients like:
- Iron – Essential for oxygen delivery to hair follicles.
- Vitamin B12 & Folate – Key for cell division and healthy hair shaft production.
- Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) – Crucial for scalp and follicle health.
Immune Involvement: The same immune mechanisms that attack the gut can sometimes trigger autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata.
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS) & Hair Health
Not everyone reacting to gluten has celiac disease. Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) can cause symptoms like fatigue, bloating, brain fog—and in some anecdotal reports—hair loss.
While there’s less scientific evidence compared to celiac disease, the proposed mechanisms include:
- Low-grade inflammation affects nutrient absorption.
- Immune-mediated effects impacting the hair cycle.
Expert Insight: According to a 2021 systematic review, more research is needed to confirm the gluten–hair loss link in NCGS.
Signs Gluten May Be Causing Your Hair Loss
You might suspect gluten as a trigger if you notice:
- Gradual thinning or sudden shedding after gluten exposure.
- Low ferritin, iron, folate, or B12 in blood tests.
- Patchy bald spots (alopecia areata) alongside digestive symptoms.
- Co-existing autoimmune disorders like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Tests to Consider:
- Celiac panel (tTG-IgA, EMA)
- Thyroid function tests (TSH, T4, TPO antibodies)
- Nutrient profile (iron, vitamin D, B12, folate, zinc)
Recovery Timeline: How Long Until Hair Regrows?
Hair regrowth after removing gluten varies depending on the severity of gut damage and nutrient depletion.
Typical Timeline:
- 0–3 months: Shedding may slow as inflammation reduces.
- 3–6 months: Nutrient levels begin to normalize; early regrowth starts.
- 6–18 months: Noticeable thickening; autoimmune patches may fill in.
- 18+ months: Full restoration is possible in many cases if scarring has not occurred.
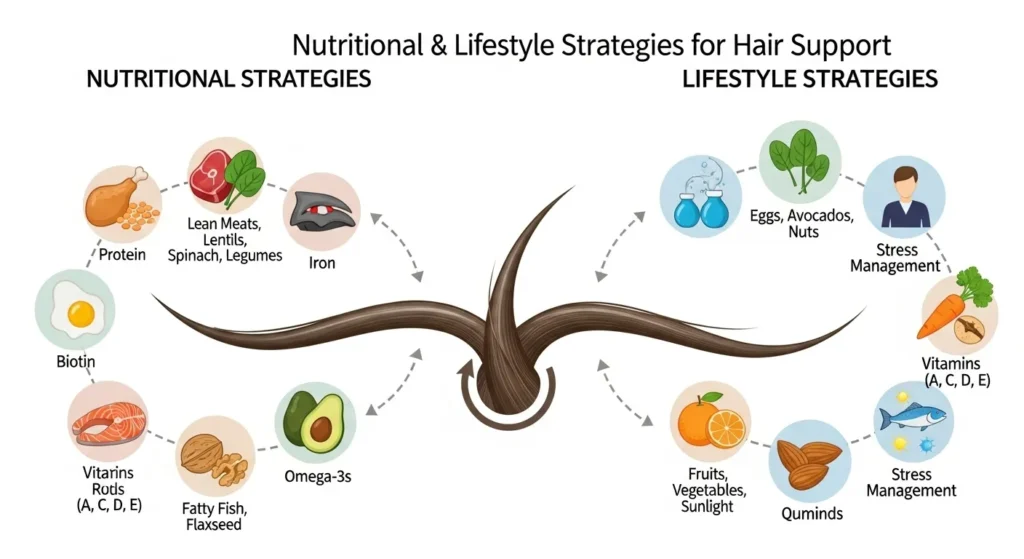
Nutritional & Lifestyle Strategies for Hair Support
Even after going gluten-free, you may need targeted nutritional support to optimize regrowth.
Key Nutrients:
- Iron & Ferritin – From lean meats, lentils, and pumpkin seeds.
- B-Complex Vitamins – From leafy greens, eggs, fortified gluten-free grains.
- Vitamin D – Sun exposure, supplements if deficient.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids – From salmon, walnuts, and chia seeds.
Lifestyle Tips:
- Practice stress-reduction techniques (yoga, meditation).
- Use gentle hair care (avoid harsh chemicals, tight hairstyles).
- Regular scalp massages improve blood flow.
When to Seek Professional Help
See a dermatologist or gastroenterologist if:
- Hair loss persists after 6–12 months of gluten-free.
- You have unexplained nutrient deficiencies.
- Patchy hair loss appears alongside other autoimmune symptoms.
Diagnostic Tools:
- Dermatologist: May perform a scalp biopsy to rule out scarring alopecia.
- Gastroenterologist: Endoscopy and biopsy for celiac confirmation.
FAQs
Q: What’s the connection between gluten and hair loss?
A: Gluten can trigger autoimmune and inflammatory responses that damage the gut, leading to nutrient deficiencies essential for hair growth.
Q: Can going gluten-free regrow hair?
A: In many celiac patients, yes—regrowth is often seen within 6–18 months if damage isn’t permanent.
Q: How long before I see improvement?
A: Some notice reduced shedding within months, but full regrowth can take over a year.
Q: Should I check my thyroid, too?
A: Yes—thyroid disorders are more common in those with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease.
Q: What if hair doesn’t regrow?
A: Explore other causes with your doctor—like hormonal changes, genetic factors, or unrelated autoimmune issues.
Take Your Next Step
Worried gluten might be behind your hair loss?
Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen. Book a consultation with Dr. Rana Irfan in Islamabad to assess nutrient levels, test for gluten sensitivity, and create a personalized regrowth plan.
