If you’re experiencing hair loss and also dealing with high or low blood pressure, you may be wondering does blood pressure cause hair loss?
This article explores the connection between blood pressure levels, medications used to manage them, and how they may impact your hair health.
You’ll learn about potential causes, treatment options, and expert-backed strategies to protect both your hair and cardiovascular wellness.
Understanding Blood Pressure and Its Role in the Body

What Is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the force of circulating blood against the walls of your arteries. It’s a vital sign that reflects how well your heart and blood vessels are working to supply oxygen to tissues, including your scalp and hair follicles.
Types of Blood Pressure
- Normal: Typically below 120/80 mmHg
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): 130/80 mmHg or higher
- Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension): Below 90/60 mmHg
How Blood Pressure Affects Circulation and Hair Follicles
Healthy blood circulation is essential for hair growth. Blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to hair follicles. Poor circulation from abnormal blood pressure, whether too high or too low, can potentially impair follicle function, leading to thinning or shedding over time.
Can Blood Pressure Cause Hair Loss?
The Connection Between High Blood Pressure and Hair Loss
High blood pressure can constrict blood vessels, reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to your scalp. Over time, this may weaken hair follicles and accelerate shedding. Some studies suggest that chronic hypertension may be linked to increased hair loss, especially in men experiencing early-onset androgenetic alopecia.
Low Blood Pressure and Its Impact on Hair Health
On the other hand, hypotension can also lead to reduced blood flow to extremities, including the scalp. Insufficient blood supply may deprive hair roots of essential nutrients, possibly leading to diffuse thinning.
Scientific Theories Behind the Link
- Vascular Insufficiency: Disrupted microcirculation in the scalp may impair follicle health.
- Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Common in hypertension, both are known to damage hair follicles.
- Hormonal Imbalance: High blood pressure and hair loss may share underlying endocrine factors, including elevated cortisol.
Role of Stress and Cortisol in Blood Pressure and Hair Loss
Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, which can contribute to both high blood pressure and telogen effluvium (a stress-induced form of hair loss). This creates a feedback loop where unmanaged stress can harm both cardiovascular and hair health.
Medications for Blood Pressure That May Trigger Hair Loss
Common Antihypertensive Drugs Linked to Hair Thinning
Several blood pressure medications list hair loss as a possible side effect. While not everyone will experience this, awareness is important.
Beta Blockers and Hair Shedding
Beta blockers like metoprolol and propranolol have been associated with hair thinning. These drugs may disrupt the hair growth cycle, especially in individuals sensitive to hormonal shifts.
ACE Inhibitors, Diuretics, and Other Possible Triggers
- ACE Inhibitors (e.g., lisinopril): Rare cases of hair loss reported.
- Diuretics (e.g., hydrochlorothiazide): May cause electrolyte imbalances that affect hair.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Less commonly reported, but still worth monitoring.
Reversible vs. Permanent Hair Loss from Medication
Hair loss caused by medications is usually telogen effluvium, a temporary condition. In most cases, hair regrows within 3–6 months after adjusting or stopping the medication under medical supervision.
Differentiating Between Hair Loss Causes
Is It Blood Pressure or Something Else?
Hair loss can have multiple triggers — genetics, hormones, stress, nutritional deficiencies, and thyroid disorders. Blood pressure may only be a part of the picture.
Diagnosing the Root Cause of Your Hair Loss
Consult a dermatologist or hair restoration expert for a full scalp assessment, blood work (including ferritin, TSH, and hormone levels), and medical history review.
The Importance of a Medical Evaluation
Self-diagnosis can lead to unnecessary treatment delays. A qualified doctor can help identify whether your hair loss is linked to your blood pressure, medications, or another issue.
How to Manage Blood Pressure Without Harming Your Hair
Natural Ways to Lower Blood Pressure
- Eat a DASH-friendly diet (rich in vegetables, lean protein, and low sodium)
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Limit alcohol and avoid smoking
- Reduce caffeine intake if you’re sensitive
Diet and Exercise Recommendations
- Include iron-rich foods like spinach and lentils to support hair health.
- Try yoga or brisk walking — both improve blood pressure and reduce stress.
Reducing Stress to Protect Your Hair and Heart
- Practice mindfulness or meditation
- Improve sleep hygiene
- Seek support if you’re facing chronic stress or anxiety
Treatment Options for Hair Loss Related to Blood Pressure
Adjusting or Switching Medications (Consult Your Doctor)
If your hair loss is suspected to be medication-related, speak to your healthcare provider about alternatives that may have fewer side effects. Do not stop medications abruptly.
Hair Regrowth Therapies
- Minoxidil (topical): Widely used for pattern hair loss
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Stimulates dormant follicles
- Microneedling: Boosts topical absorption and circulation
Nutritional Supplements for Circulatory and Hair Health
- Biotin
- Iron (if deficient)
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Zinc and Vitamin D
Role of Hair Transplant in Severe Cases
For patients with stabilized blood pressure and significant hair loss, FUE hair transplant may offer permanent restoration. Suitability should be assessed individually.
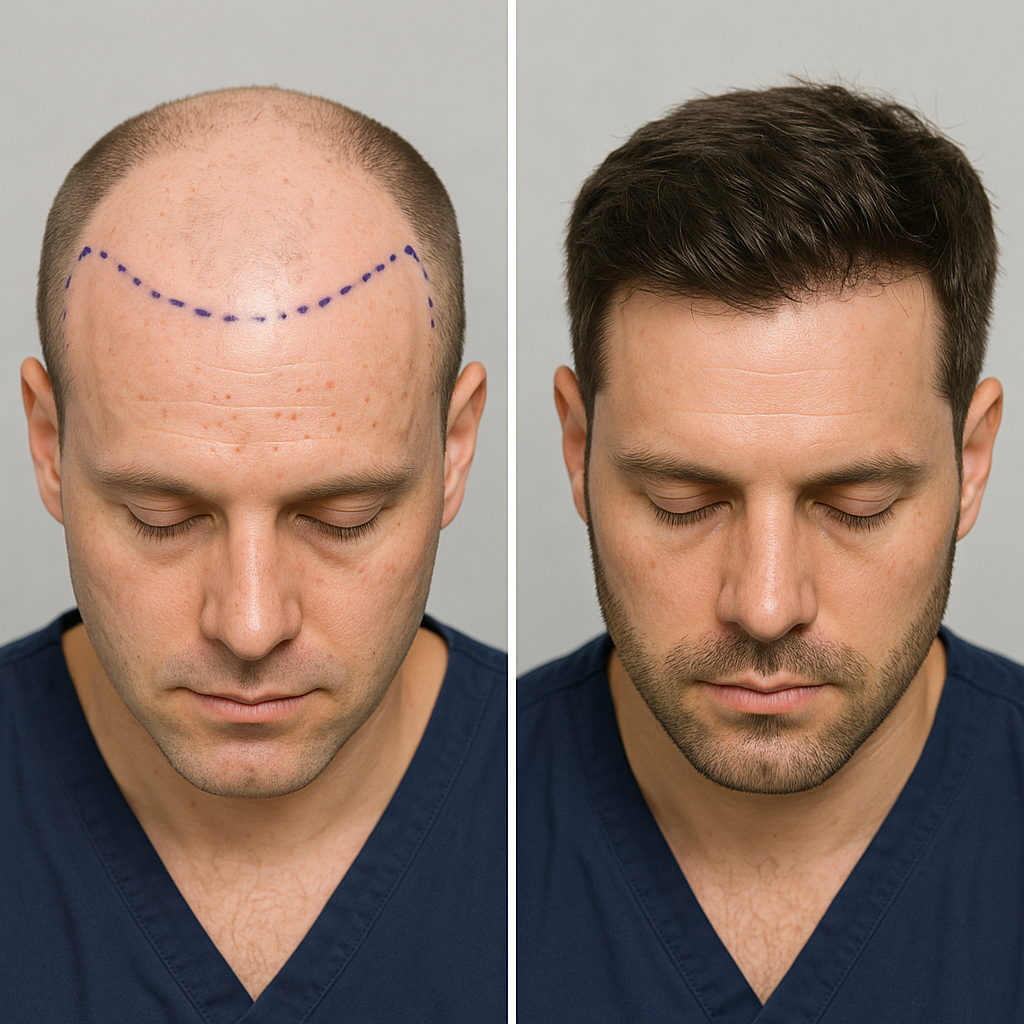
What Our Experts in Islamabad Recommend
- Maintain consistent follow-ups with both your cardiologist and hair specialist
- Do not discontinue medications without approval
- Treat hair loss early for best results
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can high blood pressure cause sudden hair loss?
Not typically. However, if high blood pressure is accompanied by extreme stress or medication side effects, it may trigger temporary hair shedding.
Is hair loss from blood pressure medication permanent?
Most cases are temporary. Hair often regrows within a few months after medication changes or lifestyle adjustments.
How long does it take for hair to regrow after stopping a medication?
Regrowth usually begins 3–6 months after stopping the medication, depending on individual health and follicle condition.
Can I prevent hair loss while managing hypertension?
Yes. Work with your doctor to find suitable medication, manage stress, and follow a balanced diet that supports both blood pressure and hair health.
Final Thoughts: Prioritize Both Hair and Heart Health
Managing your blood pressure is essential, and so is protecting your hair and confidence. With the right guidance, it’s possible to treat both issues effectively. Don’t ignore hair loss or assume it’s unrelated to your medications or circulatory health. A comprehensive evaluation can lead to solutions that support your overall well-being.
Worried about blood pressure-related hair loss?
Book a consultation with Dr. Rana Irfan, ABHRS-certified hair restoration expert in Islamabad, for a personalized evaluation and advanced hair loss treatment options tailored to your medical background.
